Technologies
Pleth Variability Index (PVi®)
A Dynamic Index for Monitoring Fluid Responsiveness with a Single Pulse Oximetry Sensor
Offered alongside Masimo SET® pulse oximetry and rainbow® Pulse CO-Oximetry, PVi provides a continuous, noninvasive measure of relative variability in the photoplethysmograph (pleth) during respiratory cycles.
PVi may be used as a dynamic indicator of fluid responsiveness in select populations of mechanically ventilated adult patients.1
Supports Clinicians in Optimizing Fluid Management
Helps Improve Outcomes in the OR and ICU
Noninvasive and Easy to Use
What Is PVi?
- PVi is a dynamic index ranging from 0 to 100 that measures the relative variability of the pleth waveform noninvasively using a single pulse oximetry sensor.
- By analyzing detected pleth amplitudes, PVi automatically calculates the dynamic changes that occur throughout the respiratory cycle.
- Increased variability in the pleth waveform has been associated with preload dependence and fluid responsiveness, making it a valuable parameter to monitor during acute care.
Note: PVi’s ability to predict fluid responsiveness may vary due to patient, procedural, and device-related factors, and fluid management decisions should be guided by a comprehensive assessment of the patient’s overall condition.
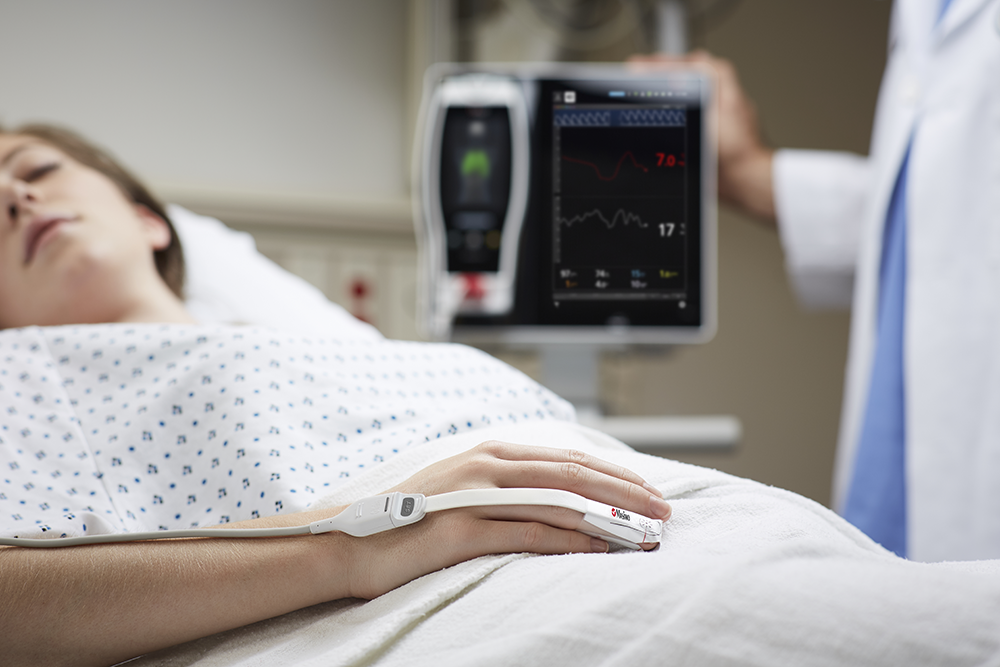
The Importance of Balanced Fluid Administration
PVi is designed to help clinicians deliver balanced fluid administration, a common intervention for enhancing cardiac output (CO). Maintaining this balance is critical, as both hypovolemia and hypervolemia can lead to adverse outcomes.2
By providing insight into a mechanically ventilated patient’s fluid responsiveness, PVi supports clinicians in improving outcomes.

Identifying Preload Dependence
Preload dependence is defined as the ability of the heart to increase stroke volume in response to an increase in preload/fluid.1
- The Frank/Starling curve defines the relationship between ventricular preload and stroke volume and the preload dependence of fluid responders.1
- During a respiration cycle, changes can be seen in the ventricular filling volume. When the preload fluid volume is low, these changes in ventricular filling volume result in higher variations in stroke volume.1
Comparing Current Standards of Care with PVi
- Traditional measurements such as SVV and PPV are obtained through an invasive arterial cannula or noninvasive blood pressure cuffs, helping clinicians assess variations in the arterial pressure waveform caused by changes in stroke volume.3
- PVi, however, leverages the arterial pleth waveform, reflecting the absorption concentration of arterial hemoglobin for a noninvasive assessment.3
Using PVi as part of fluid management protocols has been shown to improve clinical and economic outcomes while reducing fluid administration.4,5
Clinical Applications
- Hospital protocols, such as Goal-directed Therapy (GDT) and Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS), recommend fluid management as part of larger initiatives designed to improve patient care and safety.
- Proper balancing of fluids has been associated with decreased lactate build-up and shorter recovery times.4,5
GDT Outcomes*

In a study of 82 patients undergoing major abdominal surgery, researchers found that PVi-based goal-directed fluid management reduced the volume of intraoperative fluid infused and reduced intraoperative and postoperative lactate levels.4
ERAS Outcomes*
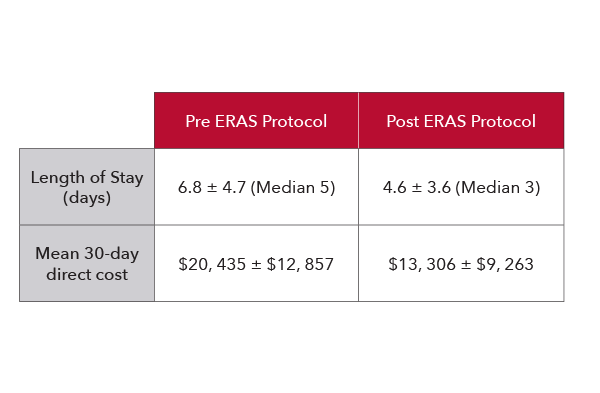
In a study of 109 patients undergoing colorectal surgery, researchers found that the implementation of an enhanced recovery protocol which included PVi led to improved patient satisfaction and substantial reductions in lengths of stay, complication rates, and costs for patients.5
SpHb® and PVi: Blood and Fluid Monitoring
PVi is available on the Masimo rainbow SET® Pulse CO-Oximetry platform alongside noninvasive, continuous monitoring of total hemoglobin, SpHb.
When monitored together, SpHb and PVi may provide clinicians with additional insight into a patient’s status.
Case Example: PVi Alongside SpHb
The following hepatic surgery case depicts the effect of dilution on total hemoglobin upon the infusion of 2.5L of crystalloid.6
Improving Patient Outcomes
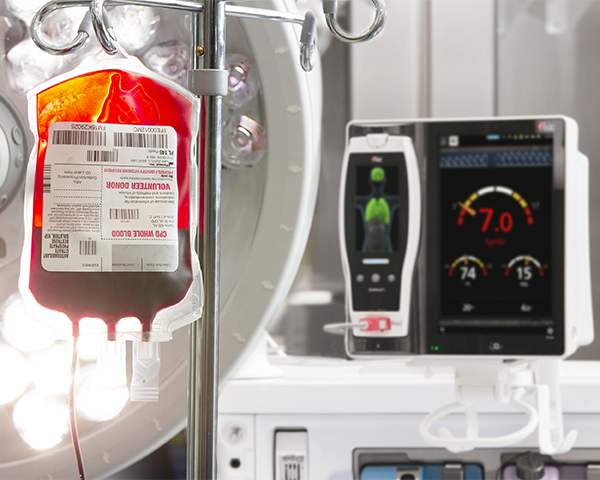
A clinical study of 18,716 patients conducted at CHU Limoges, France demonstrated the clinical value of implementing a hospital-wide GDT protocol for blood and fluid management using Masimo SpHb and PVi monitoring. Results demonstrated that monitoring with SpHb and PVi integrated in a vascular filling algorithm was associated with earlier transfusion and reduced 30- and 90-day mortality by 33% and 29%, respectively, on a whole-hospital scale.7
Numerous other studies have evaluated the utility of PVi as part of various regimens and protocols for fluid management, with varying results and outcomes.
Explore Products

Masimo SET®
Measure-through Motion and Low Perfusion™ Pulse Oximetry
Clinically proven Signal Extraction Technology® that measures accurately in challenging conditions and on all skin tones
Total Hemoglobin (SpHb®)
Noninvasive, Continuous Hemoglobin Monitoring
Monitor hemoglobin trends continuously and in real time between invasive blood samples
LiDCO® Rapid
Hemodynamic Monitoring System
Beat-to-beat advanced hemodynamic monitoring to support informed decision-making in high-acuity care areas
Schedule a Demo
Contact us today for more information on PVi.
Resources
Studies
Video
Web Pages
Materials
Cannesson et al. J Cardiothoracic 1 Vas Anes. 2010.
Bellamy MC. Br J Anaesth. 2006 Dec;97(6):755-7.
Chandler et al. J Clin Monit Comput. 2012.
Forget P et al. Anesth Analg. 2010 Oct;111(4):910-4.
Thiele RH et al. J Am Coll Surg. 2015 Apr;220(4):430-43.
Perel A. Crit Care. 2017;21:291.
Cros J, et al. J Clin Monit Comput. Aug 2019:1-9. Study utilized a goal-directed fluid therapy protocol with PVi in conjunction with a blood transfusion protocol based on SpHb.
SpHb is not intended to replace laboratory blood testing. Clinical decisions regarding red blood cell transfusions should be based on the clinician’s judgment considering among other factors: patient condition, continuous SpHb monitoring, and laboratory diagnostic tests using blood samples.
* The GDT and ERAS studies summarized above were conducted on patients undergoing a specific type of procedure and following a specific fluid management protocol. The results may not be reflective of all cases and the described GDT and ERAS protocols may not be appropriate for all types of patients and procedures.
PLCO-007660/PLM-10629B-0125